[bibshow file=http://nabis.fisi.polimi.it/data/bib/project_eschilo.bib]
Early Stage Cancer diagnosis via HIghly sensitive Lab-On-chip multitarget systems
Funding Institution: Regione Lombardia and Fondazione Cariplo, grant 2013
People: Prof. Marco Sampietro (Project leader), Prof. Riccardo Bertacco (Unit leader)
Partners: IFOM-Fondazione Istituto FIRC di oncologia Molecolare; Euroclone S.p.A.; ST Microelectronics S.r.l.
Duration: 2 years (2013-2015)
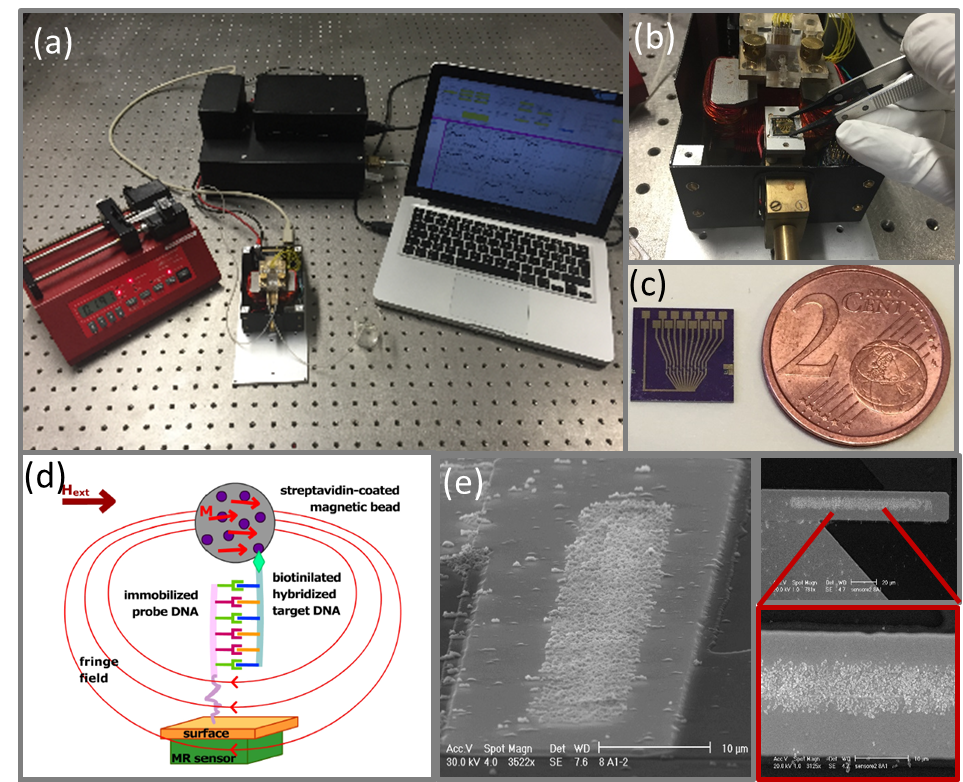
The project aims to provide an innovative, low-cost and sensitive technological platform for the early diagnosis of tumors. Starting from a small drop of blood or urine and applying proprietary techniques developed by partners in the fields of spintronics, the project aims to realize a miniaturized lab-on-chip that can identify the genetic mutations, which give rise to cancerous tumors. In this context, the project is focused on the detection of the mutation of the KRAS gene, associated to the formation of the lung adenocarcinoma. The lab-on-chip platform developed here will contain all the functionalities traditionally present in a biomedical analysis laboratory, from the capture and extraction of DNA from the biological sample to the detection and classification of the significant genetic mutations. The project will exploit a proprietary technology of the NaBis group, called “domain wall tweezers” [bibcite key=ADMA:ADMA201000146] in combination with properly functionalized magnetic particles, in order to extract the target DNA from the biological sample. This first platform will implement the “immunoaffinity capture” scheme. Then, the target DNA detection will be performed by means of a magnetic platform [bibcite key=Albisetti2013,Albisetti2014] based on magnetic tunneling junctions and magnetic nanoparticles labelling the hybridization events.
Publications
[/bibshow format=ieee process_titles=0]