[bibshow file=http://nabis.fisi.polimi.it/data/bib/project_cen2.bib]
Forces, mechanisms and pathways involved in the ATR-mediated control of nuclear plasticity in response to mechanical stress
Funding Institution: CEN – Regione Lombardia, grant 2014
People: Prof. Riccardo Bertacco (Unit leader)
Partners: IFOM-Fondazione Istituto FIRC di oncologia Molecolare; Università degli Studi di Milano; Mechanobiology Institute and Department of Biological Sciences, NUS, Singapore (collaborator); Danish Cancer Society Research Center, Copenhagen, Denmark (collaborator)
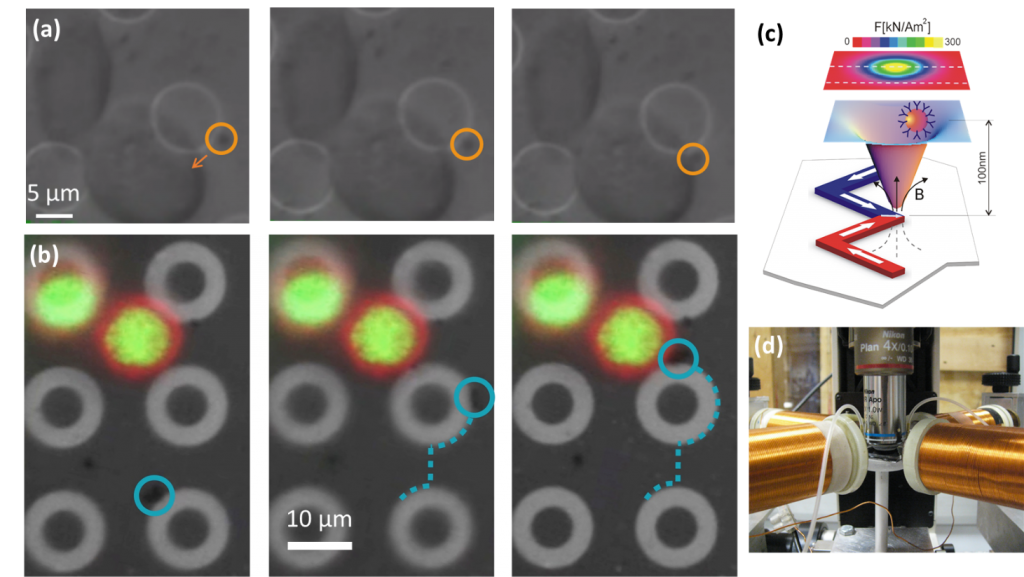
In-vitro tests and analyses are of fundamental importance for investigating biological mechanisms in cells and bio-molecules. The controlled application of forces to activate specific bio-pathways and investigate their effects, mimicking the role of the cellular environment, is becoming a prominent approach in this field. Methods based on the remote manipulation of magnetic beads are receiving great attention because magnetic fields are not screened by biological or culture media and because they do not involve relevant energy dissipation, which could eventually damage the cell structure. In this project, magnetic domain wall tweezers [bibcite key=ADMA:ADMA201000146] in combination with magnetic nanoparticles are exploited to apply controlled mechanical forces [bibcite key=Monticelli2015] to the cellular membrane. Mechanical forces owing from chromosome dynamics or plasma membrane stress convey to the nuclear envelope activating ATR. ATR is a PI3 kinase and is connect to the DNA damage response [bibcite key=Kumar], protecting the integrity of replicating chromosomes, preventing fragile site expression and aberrant condensation events. ATR coordinates nuclear envelope plasticity with chromatin and cytoskeleton dynamics to counteract aberrant chromatin dynamics at the nuclear envelopment. ATR activation will be studied using quantitative approaches to assess the mechanical forces required. The project aims at: 1) implementing nanotechnology-based tools to measure apply controlled localized mechanical forces to the cell membrane and to internal cellular compartments to activate ATR; 2) characterizing mechanisms and factors in the ATR-mediated mechanical response; 3) studying how the ATR-mechanical response affects nuclear plasticity and cytoskeleton dynamics.
Publications
[/bibshow format=ieee process_titles=0]